Cataract
What is Cataract?
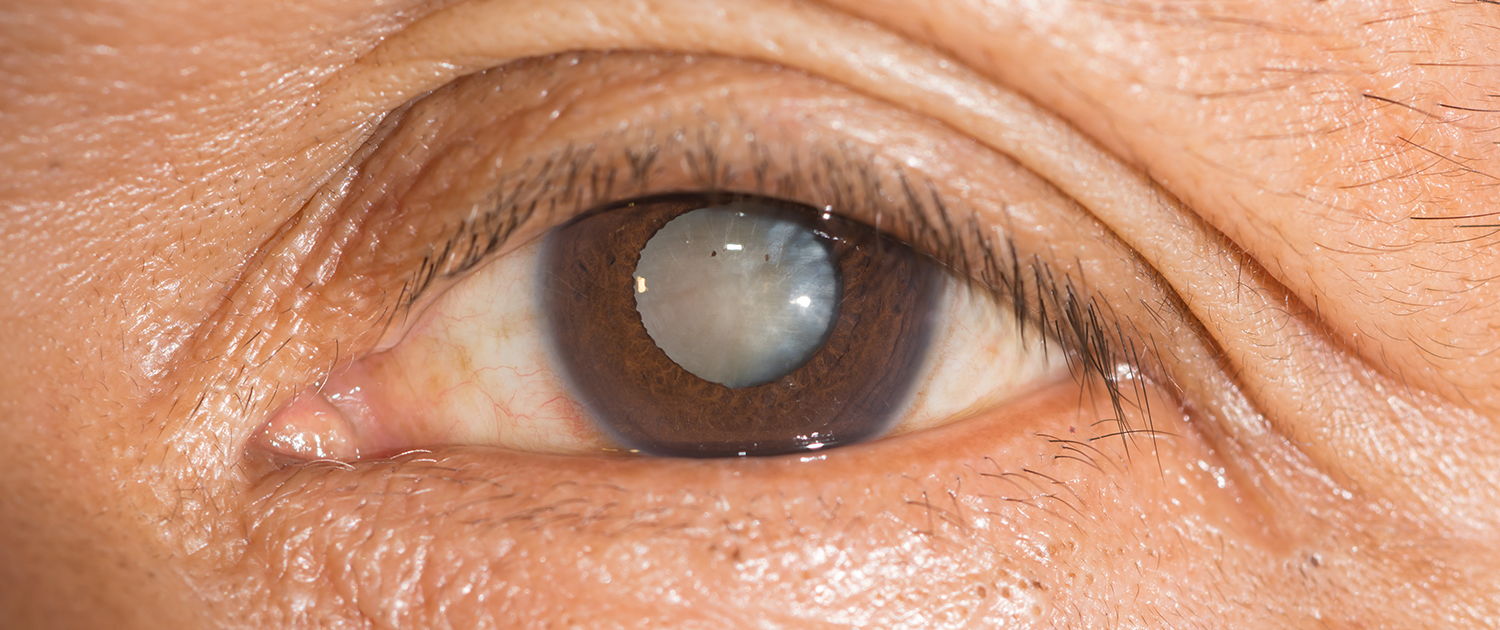
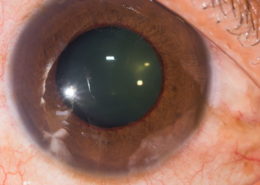
Cataract is a gradual clouding of the crystalline lens in the eye which leads to a decrease in vision. Even if it affects people of every age, cataract often develops in the third age (60 years).
Which are the symptoms of Cataract?
Due to the clouding of the crystalline lens, a small quantity of light reaches retina; as a consequence, vision and reading result to be vague and confused.
Other symptoms are:
– difficulties in reading small types (i.e. newspapers);
– trouble driving, especially at night;
– troubles with bright lights and halos around light;
– blurry vision.
What should I do if I suspect I have a cataract?
If you suspect you have a cataract, you should reserve for a medical examination in order to have an expert evaluation.
What should I expect from a cataract surgery?
It is a day surgery: during surgery, your eye is completely anaesthetised so that you can’t feel pain. Surgery usually takes about 10 or 20 minutes. Patient arrives one hour before and waits for 45 minutes after surgery before going home. Patient must not drive after the operation, but he will be probably able to drive for next day examination.
What happens during cataract surgery?
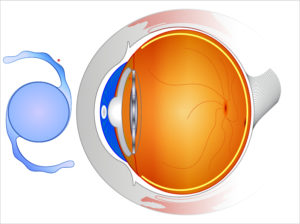
Cataract surgery consists in removing the damaged crystallin and replaced it with the implant of an artificial lens in the eye. In Fioravanti’s center we use phacoemulsification, a modern cataract surgery in which the eye’s internal lens is emulsified with an ultrasonic handpiece and aspirated from the eye. Before the surgery, a biometry exam for Intra Ocular Lens power calculation has to be done.
IOL Implants: Lens Replacement After Cataracts
An intraocular lens (or IOL) is a tiny, artificial lens for the eye. It replaces the eye’s natural lens that is removed during cataract surgery. The lens bends (refracts) light rays that enter the eye, helping you to see. Your lens should be clear. But if you have a cataract, your lens has become cloudy. Things look blurry, hazy or less colorful with a cataract. Cataract surgery removes this cloudy lens and replaces it with a clear IOL to improve your vision.
IOLs come in different focusing powers, just like prescription eyeglasses or contact lenses. Your ophthalmologist will measure the length of your eye and the curve of your cornea. These measurements are used to set your IOLs focusing power.
Monofocal IOLs
The most common type of lens used with cataract surgery is called a monofocal IOL. It has one focusing distance. It is set to focus for up close, medium range or distance vision. Most people have them set for clear distance vision. Then they wear eyeglasses for reading or close work.
Some IOLs have different focusing powers within the same lens. These are called multifocal and accommodative lenses. These IOLs reduce your dependence on glasses by giving you clear vision for more than one set distance.
Multifocal IOLs
These IOLs provide both distance and near focus at the same time. The lens has different zones set at different powers. It is designed so that your brain learns to select the right focus automatically.
Toric IOLs
For people with astigmatism, there is an IOL called toric lens. Astigmatism is a refractive error caused by an uneven curve in your cornea or lens. The toric lens is designed to correct that refractive error.
Discover the other pathologies
This post is also available in: Italian